If we suspect a Cytokine Storm.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Detecting a cytokine storm, or Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS), requires a multifaceted approach due to the complex nature of the immune system's response. CRS is characterized by an overly aggressive immune response, typically to infection or immunotherapy, leading to symptoms like fever, nausea, fatigue, and body aches. Early detection and treatment are crucial as the condition can rapidly worsen.
Elevated levels of proinflammatory cytokines that persist more than 8 months following convalescence.
"When SARS-CoV-2 infects cells expressing the surface receptors ACE2 and TMPRSS2, it is recognized by neighbouring epithelial cells, endothelial cells and alveolar macrophages, triggering the generation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines (including IL-6, IP-10 macrophage inflammatory protein 1a (MIP1a), MIP1ẞ and MCP1). These proteins attract monocytes, macrophages and T cells to the site of infection, promoting further inflammation (with the addition of IFNy produced by T cells) and establishing a pro-inflammatory feedback loop.
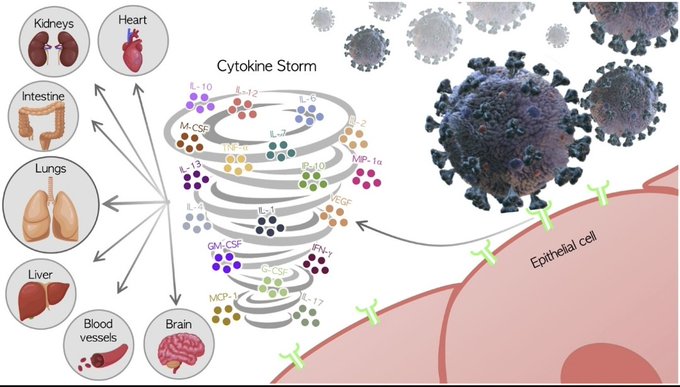
In a defective immune response (left side) this may lead to further accumulation of immune cells in the lungs, causing overproduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which eventually damages the lung infrastructure. The resulting cytokine storm circulates to other organs leading to multi-organ damage. In addition, non-neutralizing antibodies produced by B cells may enhance SARS-CoV-2 infection through antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE). further exacerbating organ damage."
The primary method for detecting cytokines is through immunoassays, with the Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) being the most common. This assay uses a primary antibody for capturing cytokines and a secondary antibody, conjugated to an enzyme or radioisotope, for detection.
Key markers of inflammation in cytokine storms include both proinflammatory cytokines such as interferon-γ (IFN-γ), interleukin-17 (IL-17), IL-1β, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10, IL-4, and IL-1ra.
Medical imaging, like chest X-rays, can also provide indications of a cytokine storm, especially in conditions like COVID-19, where lung involvement is common. However, it's important to note that the term “cytokine storm” might not always be used or diagnosed explicitly.
Regarding treatment, the role of antihistamines is notable. Histamine can initiate an abnormal immune response leading to cytokine storm and multi-organ failure. Consequently, antihistaminic medications might help in modulating the immune system, thereby aiding in the treatment of cytokine storms associated with COVID-19 and other inflammatory conditions.
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein accelerates systemic sclerosis by increasing inflammatory cytokines, Th17 cells, and fibrosis
https://journal-inflammation.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12950-023-00362-x
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Comments
Post a Comment